- Viscosity - a measure of the importance of
friction in fluid flow.
Consider, for example,
simple shear between two plates:
Consider a fluid in 2-D steady shear between two infinite plates, as shown in the sketch. The bottom plate is fixed, while the upper plate is moving at a steady speed of V.
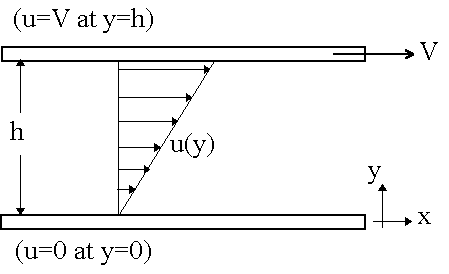
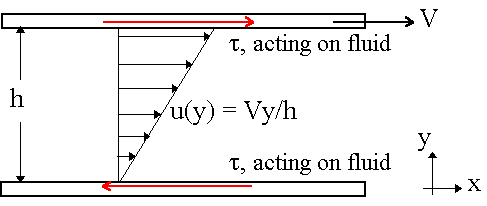
The top plate will experience a friction force to the left, since it is doing work trying to drag the fluid along with it to the right. The fluid at the top of the channel will experience an equal and opposite force (i.e. to the right). Similarly the bottom plate will experience a friction force to the right, since the fluid is trying to pull the plate along with it to the right. The fluid at the bottom of the channel will feel an equal and opposite force, i.e. to the left. In fluid mechanics, shear stress, defined as a tangential force per unit area, is used rather than force itself. Define
 (Greek letter "tau") as the
friction force per unit area acting on the fluid, as illustrated
below:
(Greek letter "tau") as the
friction force per unit area acting on the fluid, as illustrated
below:

Given: A block of weight W is sliding down an incline at constant speed V on a thin film of oil of thickness h, as sketched. Find: Speed V as a function of the other variables in the problem 
Solution: Draw a free body diagram of the block. The forces acting on the block are its weight, W, a normal force, N, due to pressure of the oil on the bottom surface of the block, and a viscous force, Fviscous, due to friction on the bottom of the block. 



- Kinematic viscosity is simply defined as the
viscosity divided by density, i.e.

- Surface tension is a property of liquids which
is felt at the interface between the liquid and another fluid
(typically a gas). Surface tension has dimensions of force per
unit length, and always acts parallel to the interface.
Surface tension causes the molecules at the interface to repel
each other, forming a kind of "skin" under tension at the interface.
A good example of surface tension is found in a common
soap bubble.
A soap bubble is a good example to illustrate the
effects of surface tension. How does a soap bubble remain spherical
in shape? The answer is that there is a higher pressure inside
the bubble than outside, much like a balloon. In fact, surface
tension in the soap film acts much the same as the tension in
the skin of a balloon. Consider a soap bubble of radius R with
internal pressure pin and external (atmospheric) pressure
pout. If the area shown is magnified, a free body diagram
of the soap film can be drawn.
On the free body diagram, the sum of all forces must be zero, since the soap film segment is not accelerating. Surface tension forces act parallel to any interface. On the free-body diagram of the soap bubble segment, there are four locations where surface tension acts, as shown. Analysis of a soap bubble yields the following,


- Surface tension (continued)
Surface tension is also important at the interface between
a liquid, a gas, and a solid. For example, a
meniscus occurs when the surface
of a liquid touches a solid wall, as most readily noticed when
a capillary tube is placed in a liquid.
Consider a glass capillary tube inserted into a liquid, such as
water. The water will rise up the tube to a height, h, because
surface tension pulls the surface of the water towards the glass,
as shown. The meniscus is the curved surface at the top of the
water column.
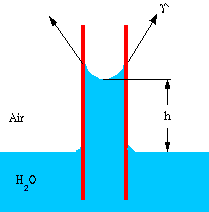
The contact angle is defined as the angle between the liquid and solid surface, as shown in the sketch. Contact angle depends on both the liquid and the solid. If theta is less than 90o, the liquid is said to "wet" the solid. However, if theta is greater than 90o, the liquid is repelled by the solid, and tries not to "wet" it. For example, water wets glass, but not wax. Mercury does not wet glass.
Consider a small glass capillary tube inserted into water. The height of the water column can be found by summing all forces acting on the water column as a free body diagram. (This is a statics problem since there is no acceleration.)Water wets glass Mercury does not wet glass 


The downward force is due to gravity, i.e. the weight of the water column. The only upward force available to balance the weight is that caused by surface tension (pressure forces all cancel out, as will be explained in a later lecture). Column height h can be predicted as follows:

- Vapor pressure is defined as the pressure at which
a liquid will boil (vaporize). Vapor pressure rises as temperature
rises.
For example, suppose you are camping on a high mountain (10,000 ft. or roughly
3,000 m in altitude). From Table A.6 the atmospheric pressure
at this elevation is about 70. kPa. From Table A.5 it is seen
that at a temperature of around 90. oC, the vapor pressure
of water is also around 70. kPa. From this it can be stated that
at 10,000 ft. of elevation, water boils at around 90 oC,
rather than the common 100 oC at standard sea level
pressure. This has consequences for cooking. For example, eggs
have to be cooked longer at elevation to become hard-boiled since
they cook at a lower temperature. A pressure cooker has the opposite
effect. Namely, the tight lid on a pressure cooker causes the
pressure to increase above the normal atmospheric value. This
causes water to boil at a temperature even greater than 100 oC;
eggs can be cooked a lot faster in a pressure cooker!
Vapor pressure is important to fluid flows because, in general,
pressure in a flow decreases as velocity increases. This can
lead to cavitation, which
is generally destructive and undesirable.
In particular, at high speeds the local pressure of a liquid sometimes
drops below the vapor pressure of the liquid. In such a
case, cavitation occurs. In other words, a "cavity"
or bubble of vapor appears because the liquid vaporizes or boils
at the location where the pressure dips below the local vapor
pressure.
Cavitation is not desirable for several reasons. First, it causes noise (as the cavitation bubbles collapse as they migrate into regions of higher pressure). Second, it can lead to inefficiencies and reduction of heat transfer in pumps and turbines (turbomachines). Finally, the collapse of these cavitation bubbles causes pitting and corrosion of blades and other surfaces nearby.